In notebook and tablet displays, the LED backlight in an LCD panel is the biggest power consumer. Although the LED backlight driver is a simple circuit, it plays a critical role in system efficiency, battery run time, thermal management and size. As screen resolution and brightness levels increase, the input power consumed by the LED backlight increases as well. Existing conventional LED drivers on the market that use a conventional single-stage architecture are reaching their peak performance and hitting their limits without any further gains in efficiency.
pSemi product line manager for power management, Jason Ngai, addresses this issue head-on in a recent EDN article. He writes how a new type of LED boost driver architecture is needed for a significant efficiency performance breakthrough, to enable low-power LCD panels for next-generation notebook and tablet designs.
His article describes a new LED boost architecture that employs a proprietary, capacitive-based charge pump circuit, and outlines its advantages over conventional LED boost drivers including lower EMI, lower output ripple and no audible noises.
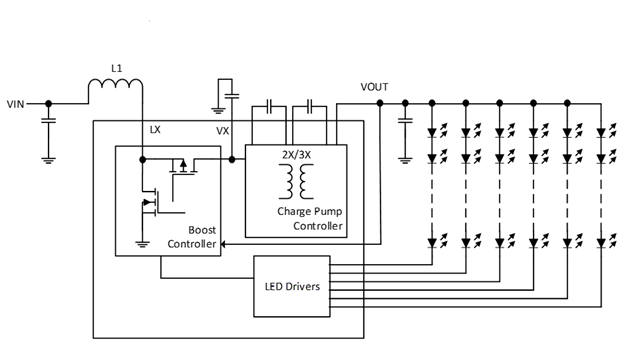
To learn more, read the full article in EDN: https://www.edn.com/led-boost-driver-architecture-improves-efficiency-of-notebook-tablet-displays/
